In this blog post, I’d like to demonstrate how you can easily wrap an OS X App for Distribution via System Center Configuration Manager. The Wrapped App can later be deployed as an Application to managed Mac Devices.
For the Wrapping you need a Windows device to install the Mac Client Installer and a Mac Device to perform the actual Wrapping.
Getting CMAppUtil
CMAppUtil, which we use for the Wrapping-Process, is part of the ConfigMgr Mac Client. The Mac Client can be found on Microsoft Download as part of the Clients for Additional Operating Systems.
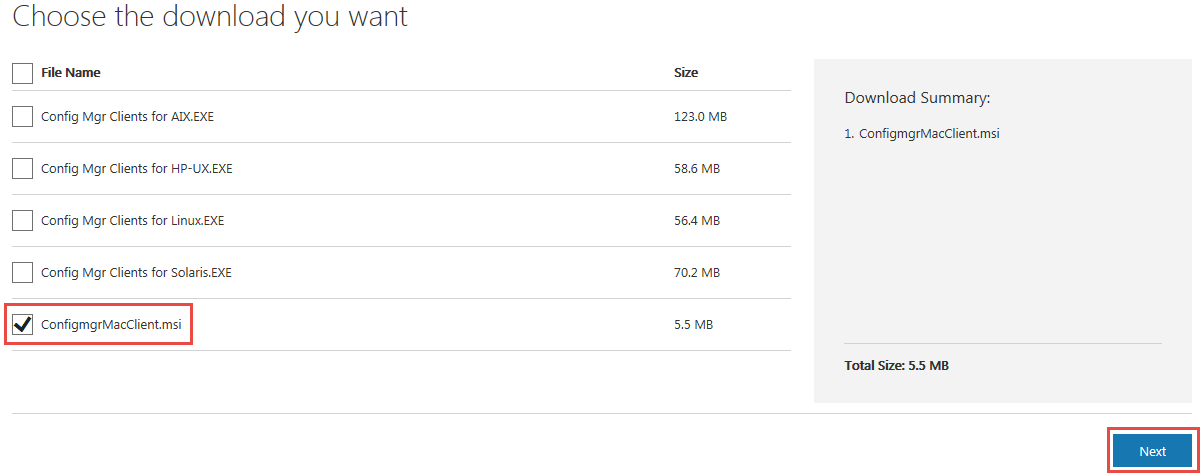
Download the ConfigmgrMacClient.msi
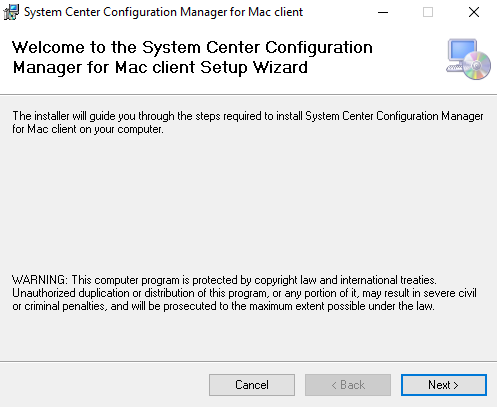
Install the “System Center Configuration Manager for Mac client Setup” on a Test device.
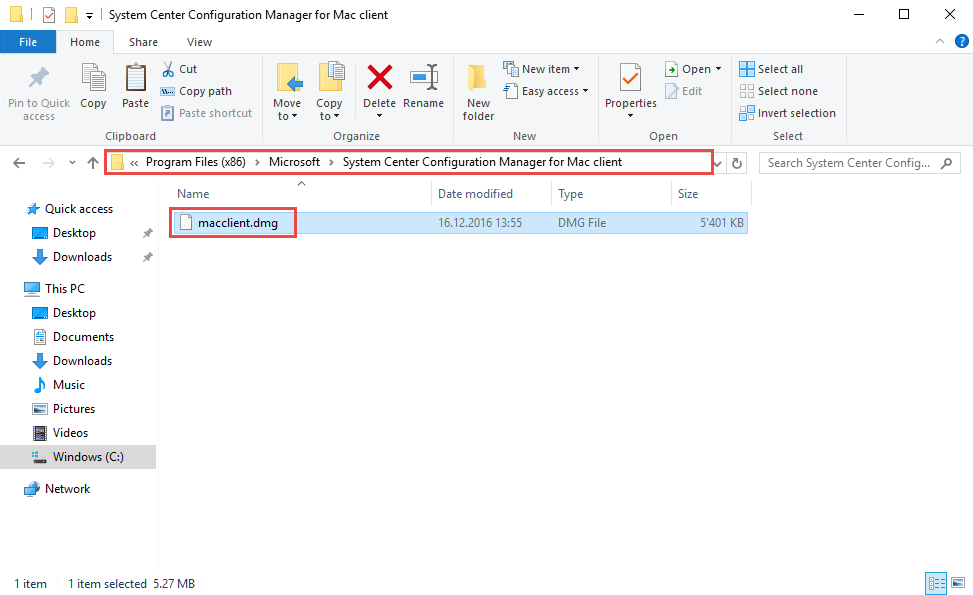
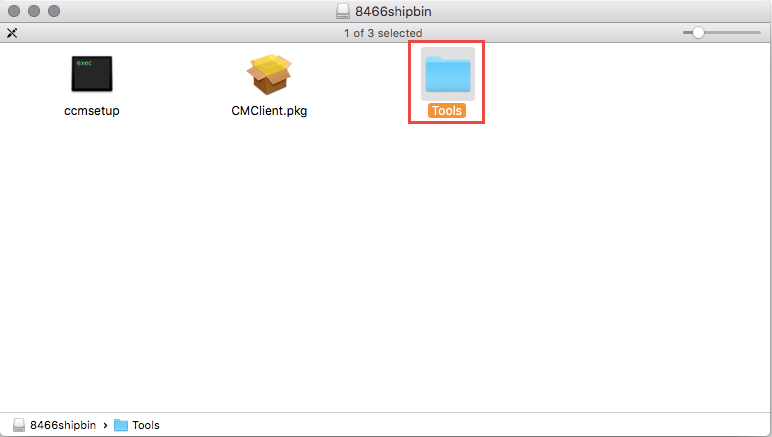
Copy the installed dmg file to a Mac OS X Device. The file is located at:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft\System Center Configuration Manager for Mac client\macclient.dmg
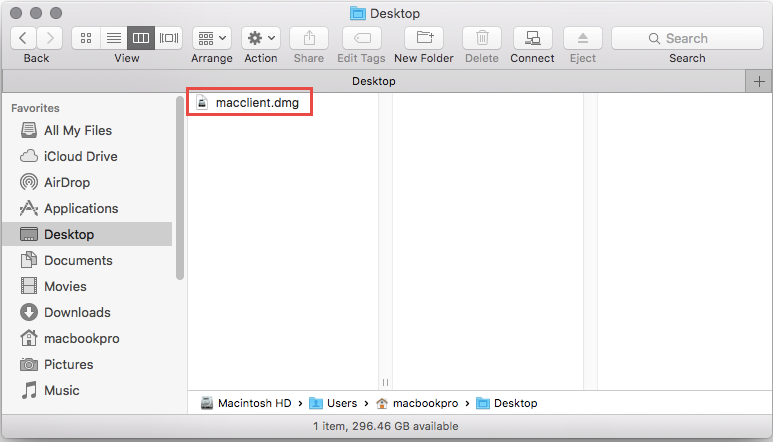
Open macclient.dmg on the Mac.
Copy the Tools folder to a place on the Mac. I use the Desktop for this example.
Getting the Apps
In this Example, we will wrap Google Chrome and Citrix Receiver. Whichever App you are going to wrap, CMAppUtil supports the following formats:
- .dmg
- .pkg
- .mpkg
- .app
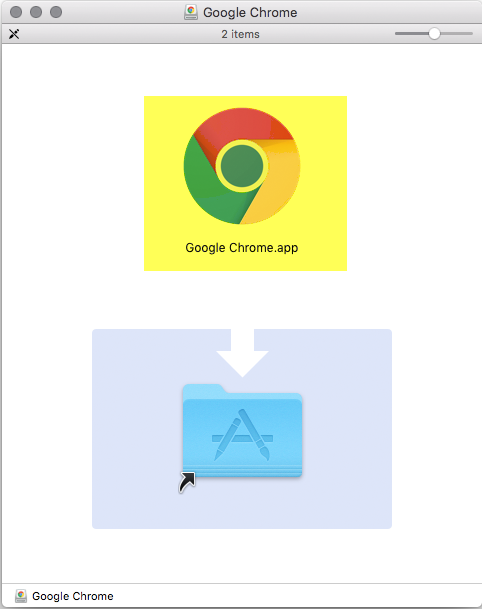
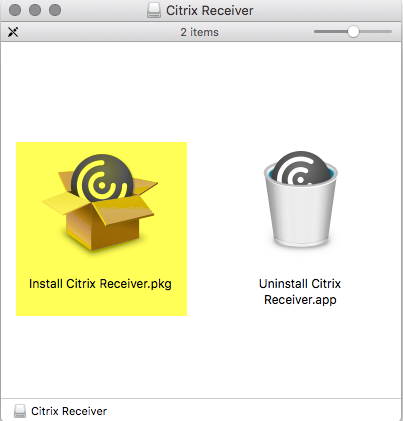
As you see the Installers for the two Applications that I choose look a bit different. Google Chrome is a native App (.app) which can just be put into the Applications Folder. Citrix Receiver however is an Installer (.pkg).
Wrapping an .app file (Google Chrome)
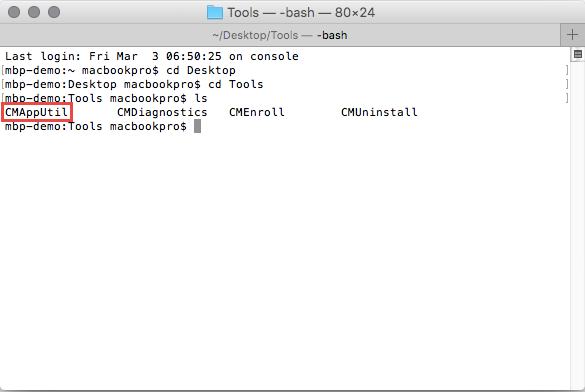
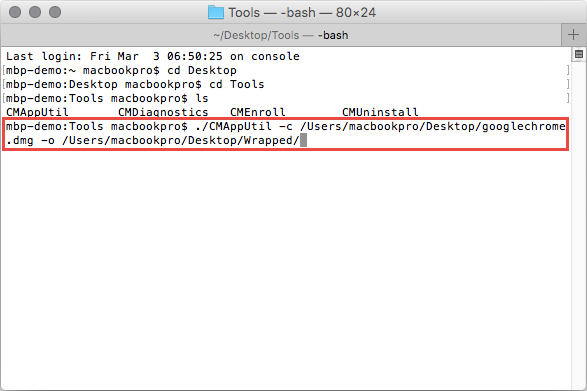
Open Terminal on the Mac and navigate into the Tools folder where CMAppUtil is located. You can use ‘cd’ to change directories and ‘ls’ to list the content of the present directory.
Use the following Command to start the Wrapping process. Adjust the Path if neededs.
./CMAppUtil -c "/Users/macbookpro/Desktop/googlechrome.dmg" -o "/Users/macbookpro/Desktop/Wrapped/"
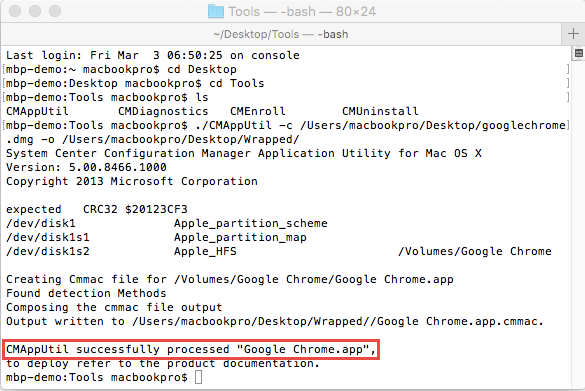
After a short while, the Wrapping Process should complete with the above message. If the dmg file is opened during the wrapping, ignore it.
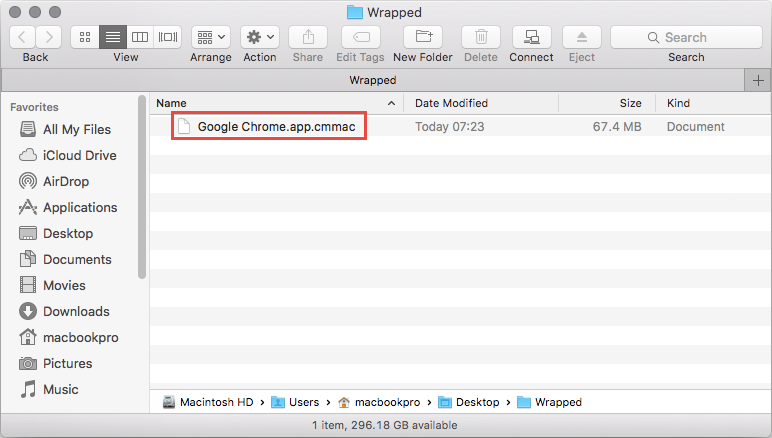
Your app should now be available in the specified Output Directory in the .cmmac format, as on the screen above. If CMAppUtil should fail, you can use the Parameter “-s” to create the cmmac with an empty detection method.
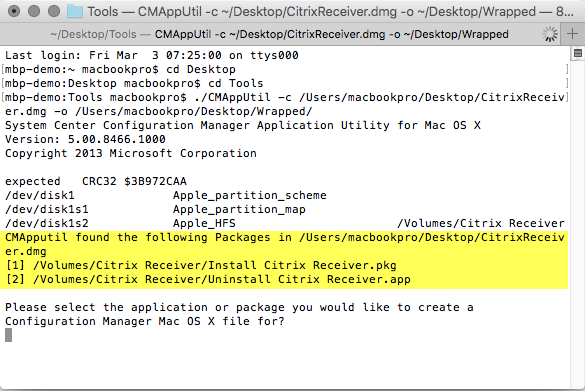
Wrapping a .pkg App (Citrix Receiver)
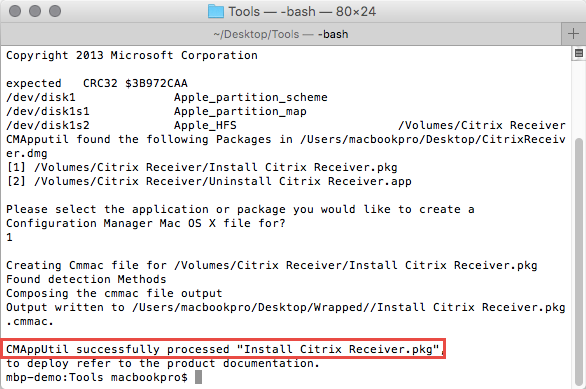
The Process of wrapping a .pkg file is exactly the same as in the example above. However, here we have the situation, that the specified .dmg has two executables in it. CMAppUtil will pause the wrapping and ask, you as seen above, to choose the correct installer. In this example 1.
You can use the parameter “-a” to convert all packages inside the .dmg file without getting the prompt below.
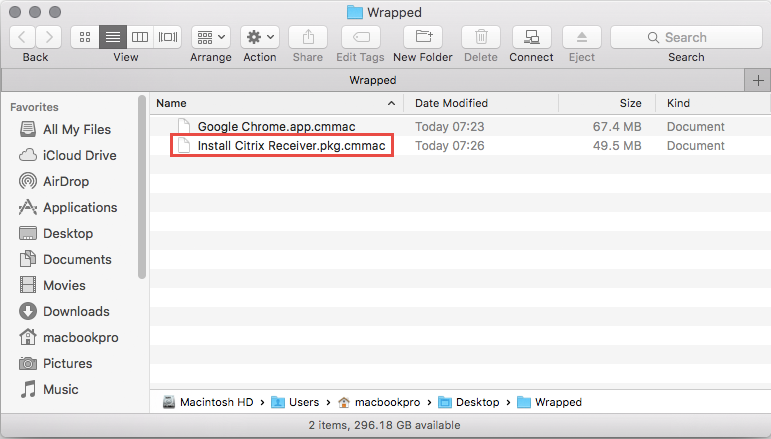
After a short while, the Wrapping should complete, leaving you with another .cmmac file in the Output Directory.
Analyzing the .cmmac file
At last, let’s have a closer look to what CMAppUtil has exactly done with the wrapped Application.
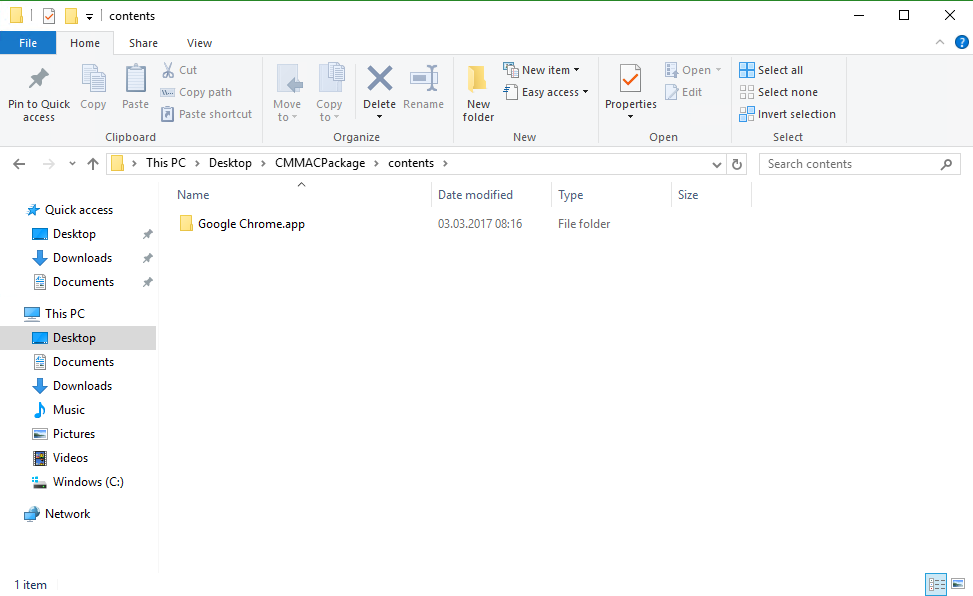
The .cmaac is an Archive File which can be opened an extract on any Windows or Mac Device.
contents: Contains the original, unmodified Installation File. In this example either “Google Chrome.app” or “Install Citrix Receiver.pkg”
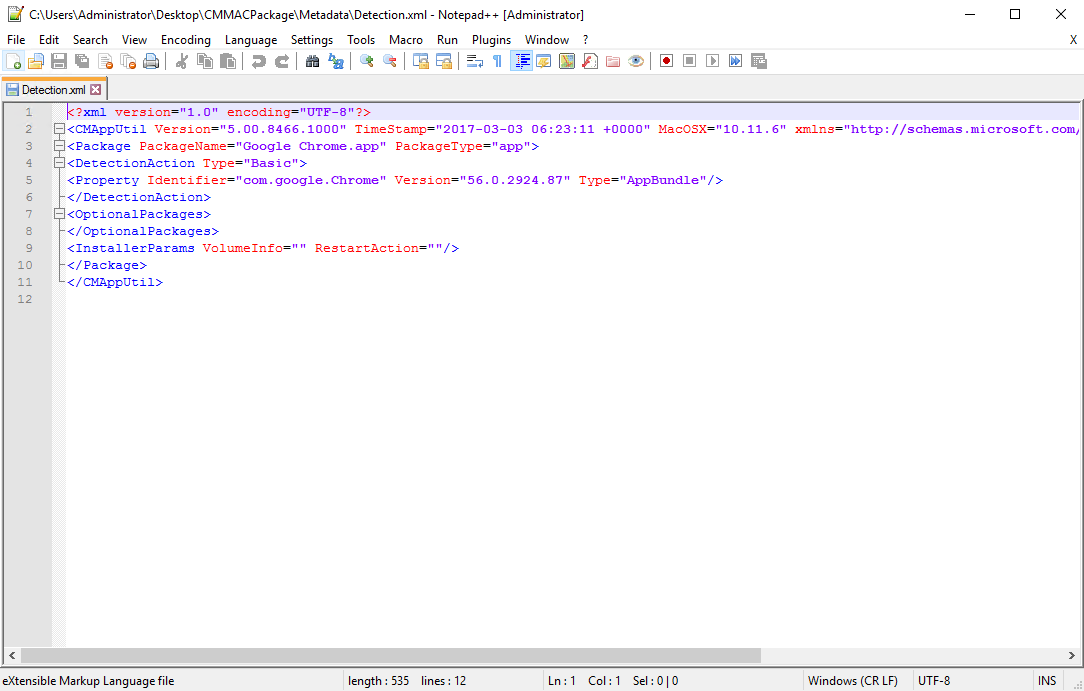
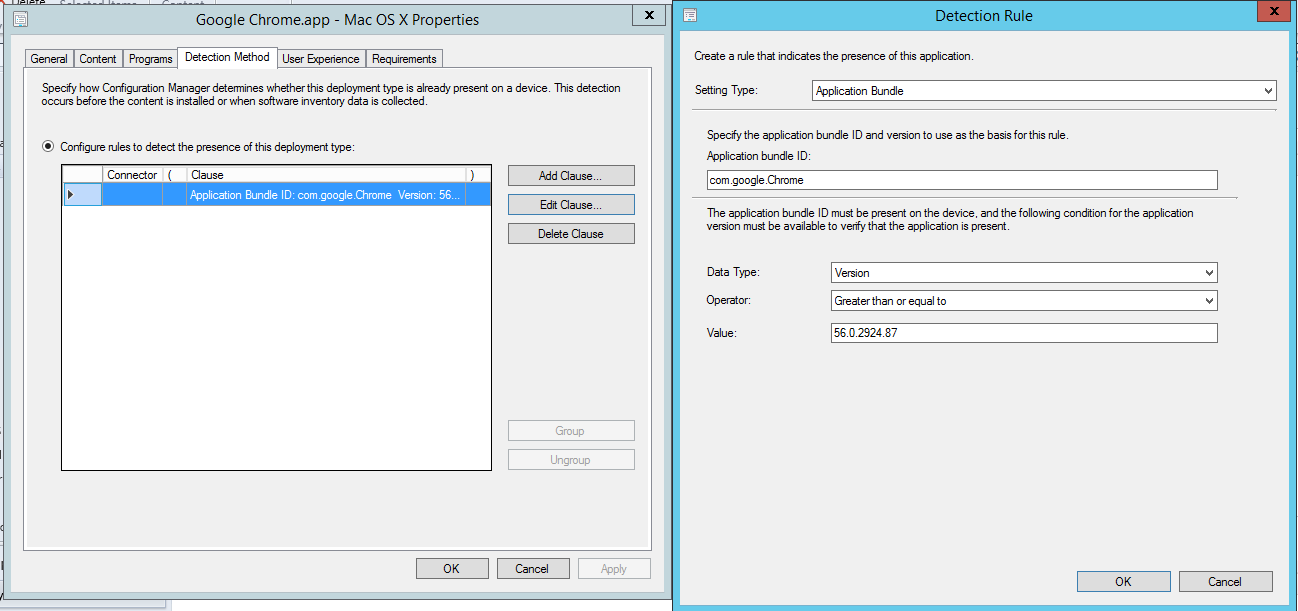
Metadata: Contains a file called Detection.xml
The Detection.xml contains, as the name implies, the Detection Method which is mandatory for creating an Application in ConfigMgr. It also contains some basic Installation Parameter as where to install the Application. Those Settings are automatically being used when importing the .cmmac file into ConfigMgr
The next blog post will be on how to create an Application within ConfigMgr and deploy this Application to a Mac, which has the Parallels Mac Management Agent installed.
Update: Thanks to Vigneshwaran for the feedback regarding the CMAppUtil Parameters.




You actually ake it appear sso easy along with yourr presentation however I to find this topic
to be actually one thing that I feel I’d never understand.
It seems too complex and extremeky huge for me.
I am taking a lopok ahead for your next put up, I’ll attempt too get the hang oof it!